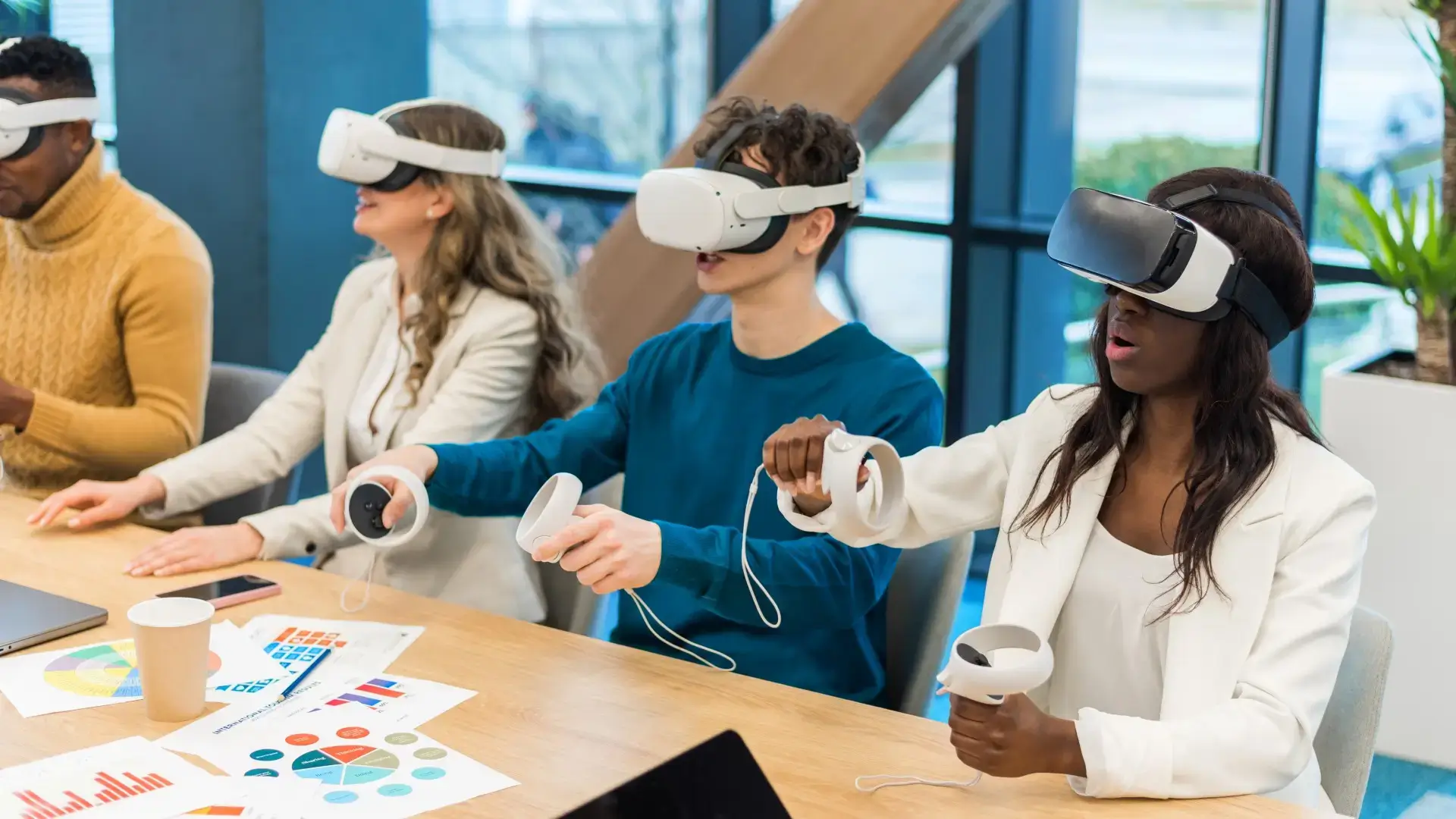
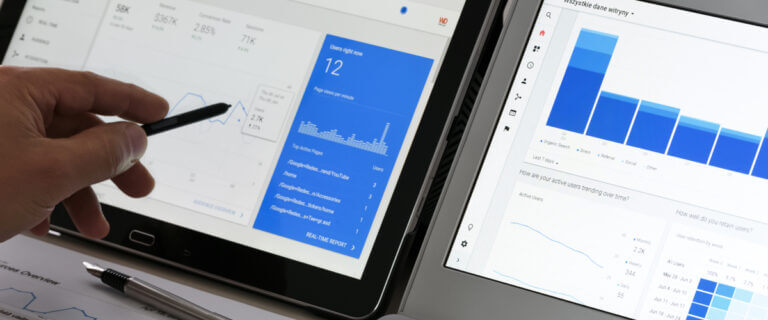
The revolutionary path of VR and AR
In the digital odyssey of the 21st century, the realms of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) have been nothing short of revolutionary. Like stepping into the OASIS of Ready Player One, where the digital world is as rich and immersive as the real one, VR and AR have undergone a metamorphosis, now standing at the forefront of technological innovation. These immersive technologies have not only expanded the horizons of gaming and entertainment but have also begun to reshape industries, redefine interactions, and reimagine the very fabric of web design.
Apple Vision Pro: Redefining digital boundaries
One of the key products gaining media attention recently is the newly launched Apple Vision Pro, which marks a significant milestone in this journey. As a beacon of immersive technology, it heralds a new chapter where the lines between the physical and digital worlds are not just blurred—they are redrawn. The Apple Vision Pro, with its advanced features and intuitive design, is poised to become a cornerstone in the evolution of web interfaces, offering a glimpse into a future where websites are not just seen but experienced.
Meta Quest 3: Democratizing virtual experiences
Amidst this transformative wave, the Meta Quest 3 emerges as another key player, further catalyzing the shift towards a more dynamic and interactive web. At a much more affordable price, Meta is predicted to gain the most public attention around VR/AR and be the key player in democratizing the use of such technologies in our daily lives. Together, these devices are not mere gadgets; they are the architects of a new era in web design—an era that beckons us to look beyond the screen and step into a world where the virtual is as tangible as the real.
As we embark on this exploration, we’ll delve into the historical context of VR and AR, chart their exponential growth, and examine how the Apple Vision Pro and Meta Quest 3 are setting the stage for a radical transformation in web design. Join us as we venture beyond the screen and into the future of web design in the age of Apple Vision Pro.
The history of VR and AR
The history of Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) indeed began in the 19th century with the advent of stereoscopic photos and viewers. This early technology allowed for the first three-dimensional visual experiences, setting the stage for the immersive technologies we see today. Over the years, VR and AR have evolved significantly, with milestones such as the Sensorama in the 1950s, the first head-mounted display (HMD) systems in the 1960s, and the rise of consumer VR headsets in the 21st century.
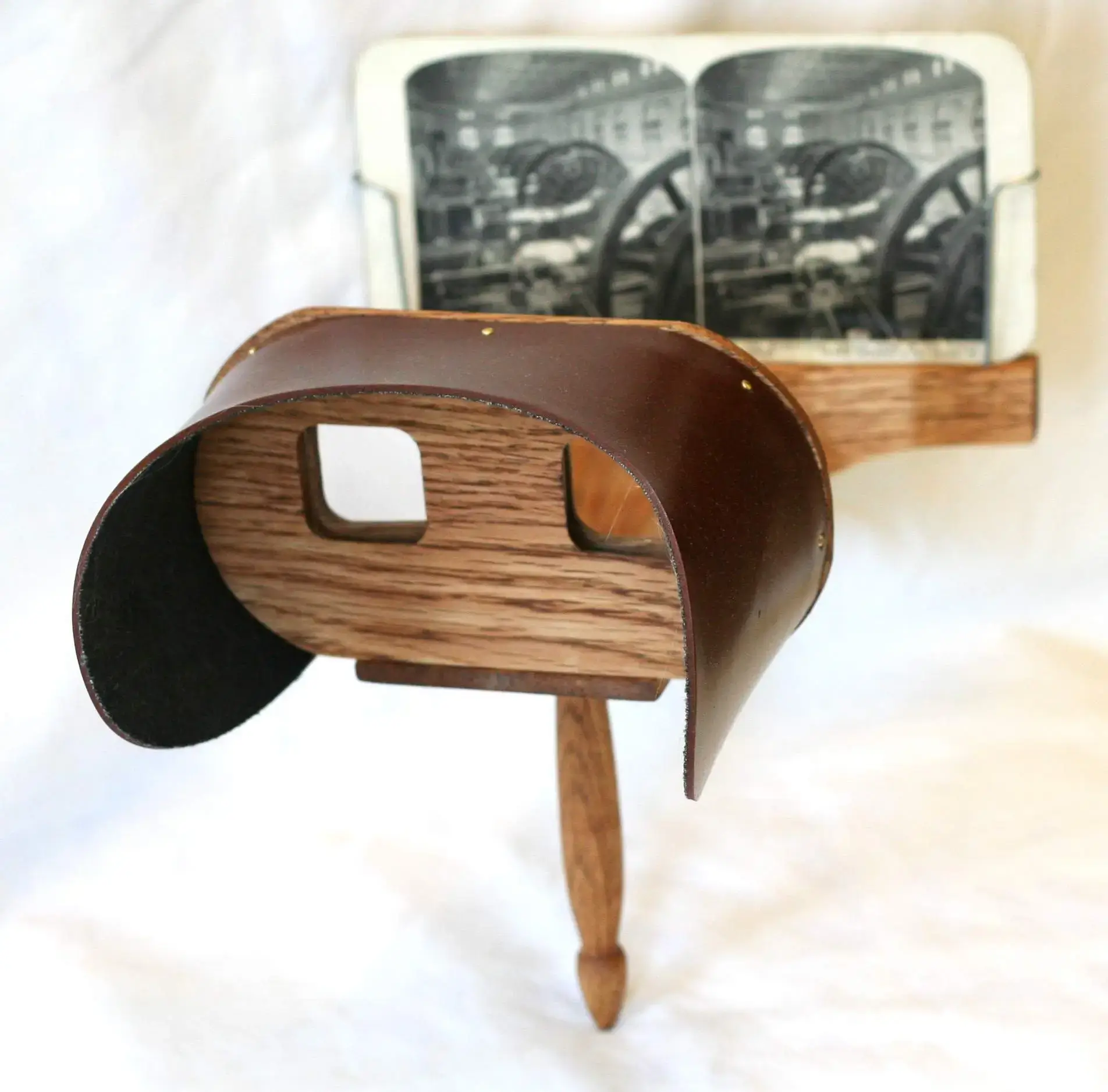

A simple double-lens device allowed viewers to experience stereo card photographs in three-dimensional depth. This method of viewing 3D photographs remained the primary mechanism to convey a sense of depth before the advent of digital technologies.

Digital evolution: The path to modern VR and AR
However, it was not until 1962 that Morton Heilig invented the Sensorama, considered the first VR machine. It combined visuals, sounds, vibrations, and even smells to create an immersive experience. This innovation was followed by the creation of the first head-mounted display in 1968, known as the Sword of Damocles. Although primitive, it paved the way for today’s advanced VR headsets.
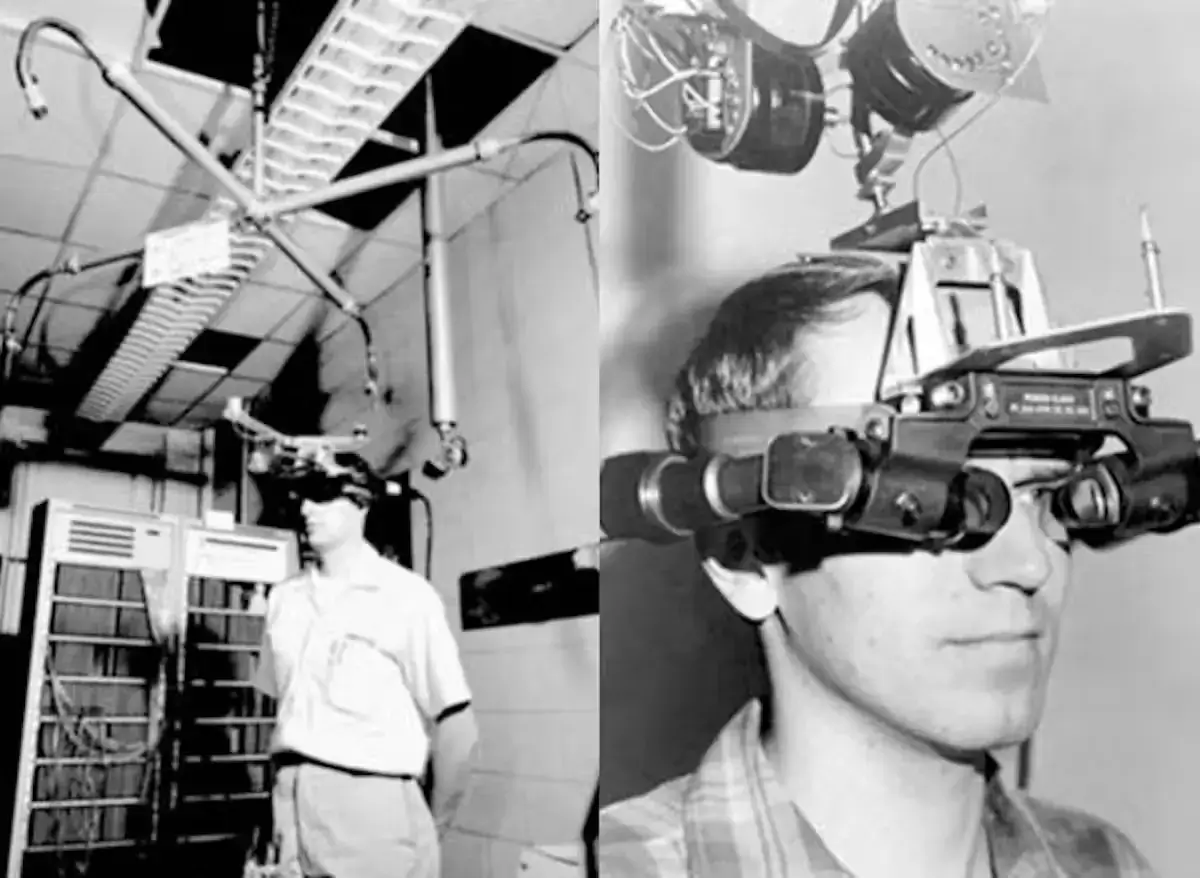

AR’s roots are similarly ancient, with early developments in the 1970s by the United States Air Force, which utilized AR for training simulations. The technology continued to evolve, but it wasn’t until the 1990s that VR and AR began to enter the public consciousness with the release of consumer products like the Nintendo Virtual Boy. Despite its commercial failure, it paved the way for the VR and AR we know today.
The renaissance of VR and AR: Entering the mainstream
Throughout the decades, virtual reality has been a rollercoaster of commercial ups and downs, mainly due to the mystique surrounding the technology while it mostly remained inaccessible to the general public. In recent years, VR and AR have experienced a renaissance, thanks to advancements in computing power, graphics, and sensor technology. Devices like the Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, and the Apple Vision Pro have brought VR and AR into the mainstream, offering experiences that are more realistic and immersive than ever before. While the technology still comes with a premium price tag, it has become more accessible to everyday home and on-the-go users.
The current state of VR and AR in web design
As we approach widespread adoption and higher public appeal, the integration of VR and AR into web design has begun to take shape, moving from experimental to mainstream. These technologies are being leveraged to create immersive brand experiences, interactive product showcases, and virtual tours that transcend traditional browsing. For instance, e-commerce sites are using AR to allow customers to visualize products in their own space before making a purchase, while educational platforms employ VR to simulate real-world scenarios for enhanced learning.
Case study: IKEA’s innovative AR shopping experience
A great example of this has been the implementation by Ikea, at the forefront of integrating AR technology into the customer shopping experience. In 2017, Ikea launched its IKEA Place app, which allowed customers to confidently experiment with and visualize how different furniture designs would transform their living spaces. The app was built on Apple’s ARKit technology, allowing users to place true-to-scale 3D models of furniture in their rooms with 98% accuracy, ensuring that the size, design, and function of each piece are just right for their space. More recently, IKEA Kreativ, an AI-powered platform, has taken this a step further by enabling customers to scan their rooms using LiDAR sensors on their iPhones & iPads, create a 3D replica of their home, and even erase existing furniture to try out new IKEA products. As the years went by and these platforms matured, they have all been integrated today into the Ikea main mobile app and website, making it convenient and easy for all potential customers to access. This level of immersive shopping experience not only enhances customer engagement but also provides a practical tool for making informed purchasing decisions from the comfort of one’s home, overcoming aspects of uncertainty and difficulty that often come with online shopping, such as ensuring the items fit one’s personal living space.

Evolving perspectives: Industry reception and challenges
The industry’s reception of VR and AR has been a mix of excitement and caution. On one hand, there are success stories like virtual real estate tours that have revolutionized property viewing, allowing potential buyers to explore spaces without physical constraints. On the other hand, the challenges of device compatibility, user accessibility, and content creation have posed hurdles to widespread adoption. This is one of many reasons why we’ve seen a conservative approach to adopting VR and AR technologies on the web by even large retail players or real estate companies.
Redefining interaction: The future of VR and AR in web design
Despite these challenges, the transformative potential of VR and AR in web design is undeniable. They offer a new dimension of interaction, where users can engage with content in a more meaningful and personal way. VR has the potential to open up an entirely new dimension of engaging content. A good example of this would be to think of a real estate platform like Zillow and its rise in social media and general popularity. While many real estate platforms today include 360-degree views of their properties, the future of real estate might well be users teleporting through virtual houses to find their dream home that can be purchased online. As we continue to witness the growth of these technologies, it’s clear that they will not only enhance the user experience but also redefine the standards of web interactions.
Immersive design: How virtual and augmented reality are revolutionizing the web
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are no longer reserved for futuristic gaming. These technologies are rapidly infiltrating web design, promising completely new ways of interacting with online content. Here’s how this transformation is happening and why it matters for the future of websites.
What is immersive design?
Immersive design breaks the barrier of the flat screen. It transports users into digital experiences that feel multidimensional and engaging. Web designers are leveraging VR and AR to replace static pages with worlds that encourage interaction and exploration.
Key ways VR and AR enhance web design
- 3D for Engagement: Gone are the days of simply looking at product images. VR and AR let customers rotate, zoom, and even “try on” items virtually before they buy, greatly enriching the online shopping experience.
- Hyper-Personalization: Imagine a website that adjusts dynamically to your interests and location. AR can achieve this— by recommending a restaurant as you pass by or guiding you through a store with targeted visuals.
- Inclusivity: These technologies make the web more accessible. People with visual impairments might interact with a website’s elements through VR-enabled audio descriptions or tactile feedback, opening up web experiences to a wider audience.
- Beyond Screens (Potentially): While still emerging, VR could make websites fully independent of a standard screen. Users might step into a full, virtual shopping mall or museum exhibit.
Meta’s proposed Metaverse
Meta Quest devices have played a pivotal role in the evolution of VR and AR technologies. From the pioneering Oculus Rift to the cutting-edge Meta Quest 3, these devices have expanded the frontiers of immersive gaming, social interaction, and professional collaboration. The Meta Quest series, especially the Quest 2, has received acclaim for its wireless design, intuitive controls, and comprehensive content library, which have made VR more accessible to a wider audience. Its affordable price, standalone setup, and user-friendly interface made it one of the most sought-after devices during the pandemic lockdown. It provided users with the opportunity to explore the outside world virtually, without the need to physically relocate or risk the health of others.
Challenges in mainstreaming VR
The journey of mainstreaming virtual reality (VR) has indeed faced its share of challenges. Despite early successes, the VR market experienced a downturn, with sales declining sharply in 2023. Meta’s substantial investment in the metaverse aimed to bring VR into the mainstream, yet the absence of a standout ‘killer app’ and the issue of an oversaturated market have been significant obstacles. The perception of VR as merely another gaming platform, coupled with concerns over comfort and immersion when compared to rivals like Xbox or PlayStation, has also dampened enthusiasm. Moreover, VR games have struggled to meet the lofty expectations set by decades of game development.
Quest Pro: Expectations vs. Reality
Criticism has also been directed at Meta’s high-priced Quest Pro device, which has been seen as offering little improvement over the Quest 2, resembling more of a developer kit than a consumer-ready productivity headset due to a lack of applications and use cases for broader adoption. However, the introduction of the Meta Quest 3, boasting enhanced resolution and Meta Reality technology, indicates Meta’s dedication to addressing these issues and reinvigorating the VR and AR markets.
Meta Quest 3 and the Future of VR
In conjunction with the release of Quest 3, Meta announced a partnership with Microsoft, which has already resulted in the integration of the Xbox Cloud Gaming streaming service into the VR headset. Additionally, Microsoft Office applications have been made available, although they have received mixed reviews, with some critics disappointed by their presentation as mere web applications repackaged as store apps.
Apple Vision Pro: A game changer
The Apple Vision Pro, launched at the beginning of 2024, has the potential to address many of Meta’s strategic shortcomings and rekindle public interest in the VR & AR space. Touted as a revolutionary device within the VR and AR landscape, Apple sets itself apart with a suite of features that redefine immersive technology. Central to the Vision Pro is a custom micro-OLED display, offering an unparalleled visual experience with a pixel count surpassing that of a 4K TV for each eye, ensuring images are crystal-clear and colors vibrant. This visual fidelity is augmented by Spatial Audio, which immerses the user in a 360-degree soundscape, heightening the sense of presence in virtual environments. Both features represent an advancement over the Meta Quest 3 headset, albeit at a premium price.
The design of the device is quintessentially Apple—sleek, elegant, and intuitive. It incorporates advanced technology into a compact form factor, featuring a three-dimensional formed laminated glass that seamlessly integrates the cameras and sensors. This design not only fulfills aesthetic purposes but also functions as an optical surface for the device’s 3D camera capabilities, enabling users to capture spatial photos and videos.
Introducing visionOS
The user interface of the Apple Vision Pro is powered by visionOS, Apple’s inaugural spatial operating system, built upon the foundations of macOS, iOS, and iPadOS. It heralds a new paradigm of interaction through eye tracking, hand gestures, and voice commands, rendering the user experience both intuitive and enchanting. Users can position apps within their space, adjust them to the ideal size, and transition between them effortlessly, effectively transforming their desktop into an infinite canvas. Herein lies Apple’s significant contribution to the web and VR space. While most popular VR headsets, such as the Meta Quest 3 or Pico 4, depend on Android’s codebase, Apple offers an alternative with a fresh perspective on spatial user interfaces. With Apple’s control over the entire software and hardware ecosystem, we witness innovative implementations of translucent, blurry window effects not previously seen on competitor Android-based devices.
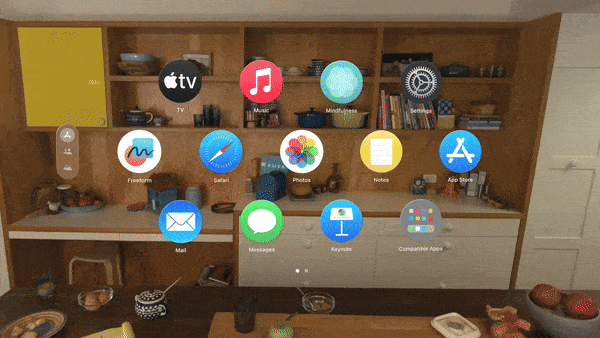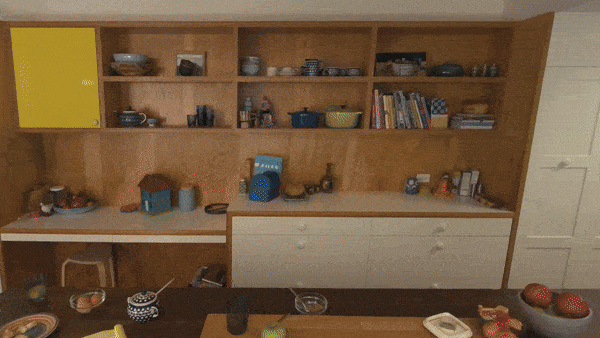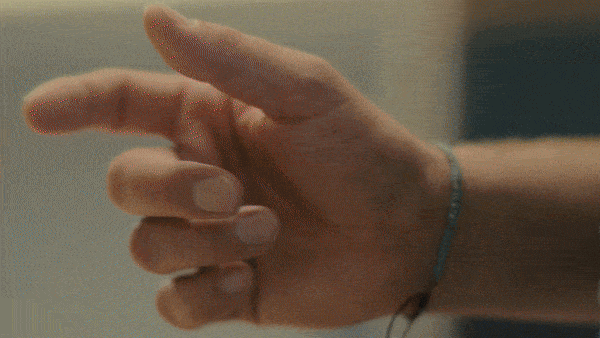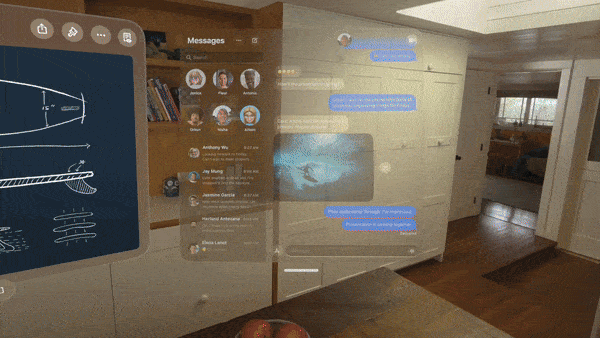
Innovative interaction and connectivity
The Vision Pro distinguishes itself from devices like the Meta Quest 3 with its innovative EyeSight feature and external display, which allow users to remain connected to their physical surroundings while engaging with virtual content. Enhanced by the device’s TrueDepth camera and LiDAR sensor, the Vision Pro offers a seamless mixed reality experience by precisely mapping the environment.
Productivity and integration into the Apple ecosystem
Not only does the Vision Pro excel in entertainment, but it also shines as a productivity powerhouse. With features like life-size FaceTime video tiles and the ability to collaborate on documents in real time, it transcends being a mere gadget. These capabilities, coupled with its seamless integration into the Apple ecosystem, herald the Vision Pro as a pivotal player in web design and a harbinger of a new era in spatial computing.
The impact of VR and AR on web design
The advent of VR and AR technologies marks a monumental shift in web design, transforming user interaction from passive observation to active engagement. This evolution transcends mere visual enhancement; it’s about crafting a multi-sensory domain where users can engage with web content in ways once relegated to the realm of fantasy.
WebVR and WebXR: Pioneering immersive web technologies
With cutting-edge devices like the Apple Vision Pro and Meta Quest 3, the possibilities for immersive web content are boundless. Envision web pages evolving beyond static displays into three-dimensional realms that users can traverse, inspect, and influence. A prime illustration of this innovation is the adoption of WebVR & WebXR technologies, as exemplified by Mozilla’s VR Hubs, which offer virtual spaces for interaction and collaboration directly within the browser.
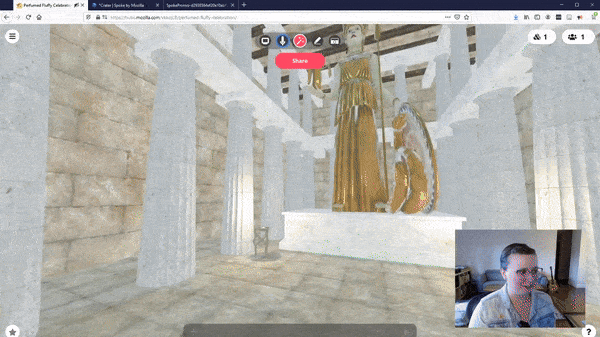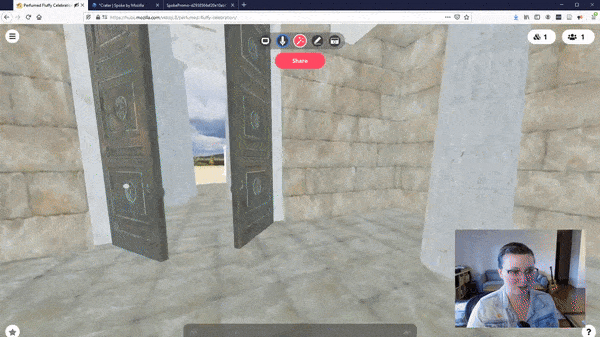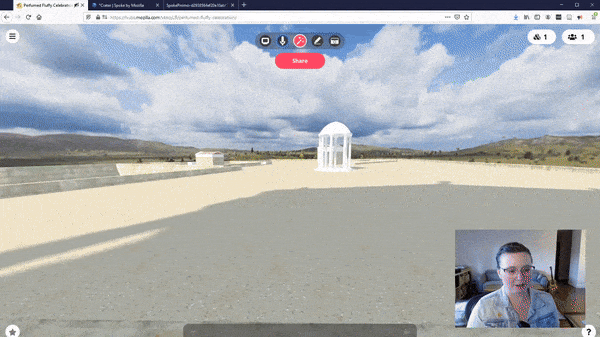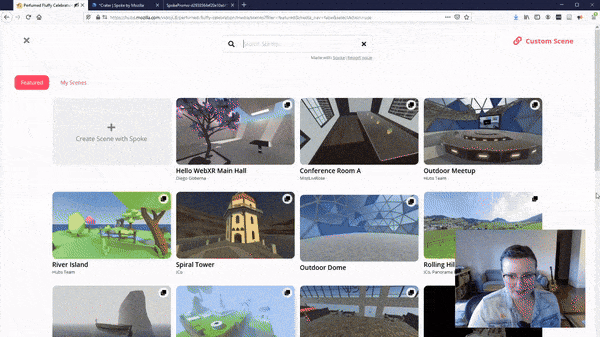
WebVR is a transformative technology that brings the immersive power of virtual reality to the web browser, eliminating the need for dedicated VR applications. It leverages the WebVR API, enabling web developers to craft interactive 3D experiences accessible through compatible browsers and viewable with VR headsets like the Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, or even simpler devices such as Google Cardboard.
Real-world applications of WebVR
Currently, WebVR offers compelling applications such as virtual tours of homes, museums, and tourist attractions, providing rich, immersive experiences without leaving home. Educational platforms are capitalizing on WebVR for interactive learning, allowing students to virtually explore historical sites or delve into complex biological systems. Additionally, learners can virtually visit historical locations or examine the human body’s anatomy in detail.
The potential for online shopping is also expanding, with the possibility of virtual storefronts where customers can try on clothes or test products in a simulated environment. Retailers are already employing WebVR to create virtual showrooms, enabling customers to navigate products in a three-dimensional space, thus enriching the online shopping experience.
The rise of WebXR and its broad implications
In the realm of immersive web technologies, WebVR is just the beginning. WebAR and WebXR are key pillars, each offering unique capabilities. WebVR primarily renders virtual reality experiences within the browser for VR headsets. In contrast, WebAR introduces augmented reality to web browsers, superimposing digital information onto the real world without requiring an app. WebXR is the most comprehensive, merging the functionalities of WebVR and WebAR to support both VR and AR experiences. It is designed to be future-proof, supporting a broad array of devices, including the Apple Vision Pro, which added support shortly after its release.
WebXR stands out for its compatibility with a diverse array of headsets and platforms, a web standard years in the making and successor of WebVR & WebAR. The support of WebXR includes the stable versions of Edge, Chrome 79+, Opera 66+, Samsung Internet 12+, and Oculus Browser. It’s also set to be supported in Safari for visionOS on the Apple Vision Pro mixed reality headset. This extensive compatibility positions WebXR as a versatile tool for developers eager to craft cross-platform immersive experiences. While WebVR and WebAR still hold value, they offer more limited support and are gradually being eclipsed by the more sophisticated capabilities of WebXR.
These technologies demonstrate the versatility and potential of web-based immersive technologies to revolutionize our interaction with digital content across various sectors. They pave the way for more personalized web experiences and immersive brand interactions.
Personalized experiences and spatial design
VR and AR enable web design to adapt to individual user preferences and behaviors, providing customized content that boosts usability and satisfaction. For example, a fitness website could offer personalized workout environments and stream demo sessions without requiring downloads, or a music platform might enable users to attend virtual concerts.
Furthermore, VR and AR are reshaping web design principles, encouraging designers to move beyond traditional layouts to spatial design. As users grow accustomed to the interactivity of VR and AR, their expectations for web browsing evolve, seeking more engaging and responsive interfaces.
Ultimately, VR and AR are redefining not only our perception of the web but also our interaction with it, establishing new standards for web design. For designers, the challenge is to craft for the future, bridging the gap and facilitating seamless transitions between devices and visual environments, making users feel at ease in the burgeoning immersive world of augmented and virtual reality. As these technologies advance, they promise to open up novel creative possibilities, redefine user engagement, and shape the future of the digital experience.
Challenges and considerations
The integration of VR and AR into web design brings a host of challenges. Designers must navigate technical obstacles such as cross-device compatibility and the high computational demands of immersive experiences. High-resolution graphics and real-time rendering can tax servers and devices, requiring a delicate balance between visual quality and performance.
Technical obstacles and performance optimization
One particular challenge is the current low fidelity of 3D objects and effects that can be reasonably rendered on standalone headsets with less powerful processors. This can be a setback for consumers accustomed to hyper-realistic gaming or productivity environments. If the benefits of under-developed and under-optimized games or virtual environments are not immediately apparent, or if the immersive elements fail to engage, users may view them as a regression. For example, PlayStation and Xbox are renowned for their immersive graphics, while Nintendo is celebrated for its simple, cartoon-like aesthetic that still delivers an entertaining gaming experience.
In productivity software, users desire control over their creations, and visual and performance limitations can stifle creativity, particularly when the advantages of spatial computing are not evident. Spatial computing is beneficial for collaborative projects, group meetings, or presenting 3D models. Still, without a community, it doesn’t offer an immediate advantage, which is a significant barrier to the widespread adoption of the Metaverse concept. To fulfill promises of greater immersion and interaction, it’s crucial for users to feel comfortable, regardless of the initial graphical appeal.
The demand for specialized Skills in spatial computing
Specialized skills are increasingly in demand as VR and AR web design extend beyond traditional 2D interfaces. Designers need proficiency in spatial design, 3D modeling, and user interaction within three-dimensional spaces. This skill set is still relatively scarce, necessitating education and training to prepare designers for this new paradigm.
Ensuring user accessibility and comfort
User accessibility is another vital aspect. VR and AR design requires a thorough understanding of user ergonomics and comfort to prevent discomfort or motion sickness. Designers must possess the technical skills to simplify and optimize three-dimensional content for VR headsets, which may involve aesthetic compromises or advanced VR optimization techniques to deliver content promptly. Additionally, making these experiences universally accessible, including for users with disabilities, is essential for inclusive design.
Technology and tools for overcoming design challenges
Devices like the Apple Vision Pro and Meta Quest 3 are addressing some of these challenges by offering intuitive design tools and platforms that streamline the creation of VR and AR content. Their sophisticated sensors and user interface technologies contribute to more accessible and comfortable experiences. However, having more technology at one’s disposal is not sufficient to motivate designers and developers to engage. The industry must continue to progress, establishing standards and best practices to guide designers in creating VR and AR experiences that are captivating, accessible, and user-friendly.
Looking ahead, it’s evident that VR and AR will significantly impact web design. The industry must rise to these challenges, driving innovation while ensuring that these potent technologies are utilized responsibly and inclusively.
Future predictions
As we gaze into the digital horizon, it’s clear that the path of web design is inexorably intertwined with VR and AR technologies. The ongoing evolution and adoption of devices like the Apple Vision Pro and Meta Quest 3 are primed to catalyze a fundamental shift in our conception and interaction with the web.
Enhanced sensor integration and privacy considerations
Another trend on the rise is the increasing comfort and familiarity with using cameras and gyroscopic sensors across the internet. This could manifest as automatic opt-ins for websites to access such devices, or as wearable technology becomes more prevalent, users may consent to constant sensor access by apps or websites. This shift is poised to boost the adoption of VR or AR websites and platforms, streamlining the user experience by eliminating the need for additional permissions. While this raises potential privacy concerns, future sensor use will lively mirror our current relationship with multi-camera devices, with privacy-conscious individuals taking measures to shield their lenses as needed, and others accepting the trade-off for a fully functional experience.
Spatial design and three-dimensional interfaces
Looking ahead, web design is set to transcend traditional two-dimensional interfaces, adopting spatial design principles for more natural and intuitive interactions. Websites could evolve into immersive environments that respond to user movement and gestures, with dynamic backgrounds and floating content. The role of web designers will evolve to focus on creating virtual spaces that are as navigable and comfortable as they are visually engaging. The resurgence of parallax effects in the mid-2020s is a precursor to this shift, introducing more depth and setting the stage for a “layered” user interface design.
The impact of devices like the Apple Vision Pro will likely influence emerging design trends that emphasize spatial awareness and three-dimensional storytelling. User interfaces will evolve to leverage VR and AR capabilities such as gaze tracking and spatial audio, providing a more personalized and immersive experience.
Beyond the screen: The web as a mixed reality platform
Furthermore, the digital landscape may extend beyond traditional screens as mixed reality becomes a staple of everyday life. The web could act as a conduit between the physical and virtual realms, with AR overlays offering contextual information in real-time, and VR spaces providing portals to alternative realities.
The future of web design is bound only by the limits of imagination, with VR and AR technologies unlocking unprecedented avenues for creativity, connection, and discovery. As we embrace these innovations, the web is set to transform from a mere informational tool into a canvas for experiences that profoundly enrich our lives.
Conclusion
As we stand on the brink of a new digital era, the transformative potential of VR and AR technologies in web design is both profound and thrilling. Devices like the Apple Vision Pro and Meta Quest 3 are more than mere tools; they are the forerunners of a future where our web interactions are as rich and immersive as our real-world experiences. They herald a web that is more engaging, interactive, and human-centric.
For web designers and developers, this marks a pivotal moment. The emergence of VR and AR technologies presents an unparalleled opportunity to escape the flat confines of the screen and create truly three-dimensional experiences. It’s a call to innovate, experiment, and push the boundaries of web design.
The road ahead is fraught with challenges, yet it is also replete with boundless opportunities. By embracing VR and AR, designers and developers can forge web experiences that are not merely observed or listened to, but felt and lived. As we venture into the future, let us do so with a sense of wonder, a zeal for exploration, and a dedication to crafting a more immersive, intuitive, and impactful web than ever before.